# 🪄 Testing with AI
CodeceptJS is the first open-source test automation framework with AI features to improve the testing experience. CodeceptJS uses AI provider like OpenAI or Anthropic to auto-heal failing tests, assist in writing tests, and more...
Think of it as your testing co-pilot built into the testing framework
🪄 AI features for testing are experimental. AI works only for web based testing with Playwright, WebDriver, etc. Those features will be improved based on user's experience.
# How AI Improves Automated Testing
LLMs like ChatGPT can technically write automated tests for you. However, ChatGPT misses the context of your application so it will guess elements on page, instead of writing the code that works.
CodeceptJS can share the testing context with AI provider when asked questions about a test.
So, instead of asking "write me a test" it can ask "write a test for this page". GPT knows how to write CodeceptJS code, how to build good-looking semantic locators and how to analyze HTML to match them. Even more, GPT suggestions can be tested in real-time in a browser, making a feedback loop.
CodeceptJS AI can do the following:
- 🏋️♀️ assist writing tests in
pause()or interactive shell mode - 📃 generate page objects in
pause()or interactive shell mode - 🚑 self-heal failing tests (can be used on CI)
- 💬 send arbitrary prompts to AI provider from any tested page attaching its HTML contents
# How it works
As we can't send a browser window with ChatGPT we are not be able to fully share the context. But we can chare HTML of the current page, which is quite enough to analyze and identify if a page contains an element which can be used in a test.
AI providers have limits on input tokens but HTML pages can be huge. However, some information from a web page may be irrelevant for testing. For instance, if you test a blog, you won't need text contents of a post, as it can't be used in locators. That's why CodeceptJS sends HTML with all non-interactive HTML elements removed. So, only links, buttons, fields, etc will be sent to AI as a context. In case you have clickable <div> but with no role="button" it will be ignored. Also, we minify HTML before sending.
Even though, the HTML is still quite big and may exceed the token limit. So we recommend using models with at least 16K input tokens, (approx. 50K of HTML text), which should be enough for most web pages. It is possible to strictly limit the size of HTML to not exceed tokens limit.
❗AI features require sending HTML contents to AI provider. Choosing one may depend on the descurity policy of your company. Ask your security department which AI providers you can use.
# Set up AI Provider
To enable AI features in CodeceptJS you should pick an AI provider and add ai section to codecept.conf file. This section should contain request function which will take a prompt from CodeceptJS, send it to AI provider and return a result.
ai: {
request: async messages => {
// implement OpenAI or any other provider like this
const ai = require('my-ai-provider')
return ai.send(messages)
}
}
In request function messages is an array of prompt messages in format
;[{ role: 'user', content: 'prompt text' }]
Which is natively supported by OpenAI, Anthropic, and others. You can adjust messages to expected format before sending a request. The expected response from AI provider is a text in markdown format with code samples, which can be interpreted by CodeceptJS.
Once AI provider is configured run tests with --ai flag to enable AI features
npx codeceptjs run --ai
Below we list sample configuration for popular AI providers
# OpenAI GPT
Prerequisite:
- Install
openaipackage - obtain
OPENAI_API_KEYfrom OpenAI - set
OPENAI_API_KEYas environment variable
Sample OpenAI configuration:
ai: {
request: async messages => {
const OpenAI = require('openai')
const openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: process.env['OPENAI_API_KEY'] })
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages,
})
return completion?.choices[0]?.message?.content
}
}
# Mixtral
Mixtral is opensource and can be used via Cloudflare, Google Cloud, Azure or installed locally.
The simplest way to try Mixtral on your case is using Groq Cloud (opens new window) which provides Mixtral access with GPT-like API:
Prerequisite:
- Install
groq-sdkpackage - obtain
GROQ_API_KEYfrom Groq Cloud - set
GROQ_API_KEYas environment variable
Sample Groq configuration with Mixtral model:
ai: {
request: async messages => {
const Groq = require('groq-sdk')
const client = new Groq({
apiKey: process.env['GROQ_API_KEY'], // This is the default and can be omitted
})
const chatCompletion = await groq.chat.completions.create({
messages,
model: 'mixtral-8x7b-32768',
})
return chatCompletion.choices[0]?.message?.content || ''
}
}
Groq also provides access to other opensource models like llama or gemma
# Anthropic Claude
Prerequisite:
- Install
@anthropic-ai/sdkpackage - obtain
CLAUDE_API_KEYfrom Anthropic - set
CLAUDE_API_KEYas environment variable
ai: {
request: async messages => {
const Anthropic = require('@anthropic-ai/sdk')
const anthropic = new Anthropic({
apiKey: process.env.CLAUDE_API_KEY,
})
const resp = await anthropic.messages.create({
model: 'claude-2.1',
max_tokens: 1024,
messages,
})
return resp.content.map(c => c.text).join('\n\n')
}
}
# Azure OpenAI
When your setup using Azure API key
Prerequisite:
- Install
@azure/openaipackage - obtain
Azure API key,resource nameanddeployment ID
ai: {
request: async messages => {
const { OpenAIClient, AzureKeyCredential } = require('@azure/openai')
const client = new OpenAIClient('https://<resource name>.openai.azure.com/', new AzureKeyCredential('<Azure API key>'))
const { choices } = await client.getCompletions('<deployment ID>', messages)
return choices[0]?.message?.content
}
}
When your setup using bearer token
Prerequisite:
- Install
@azure/openai,@azure/identitypackages - obtain
AZURE_TENANT_ID,AZURE_CLIENT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET
ai: {
request: async messages => {
try {
const { OpenAIClient } = require('@azure/openai')
const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require('@azure/identity')
const endpoint = process.env.API_ENDPOINT
const deploymentId = process.env.DEPLOYMENT_ID
const client = new OpenAIClient(endpoint, new DefaultAzureCredential())
const result = await client.getCompletions(deploymentId, {
prompt: messages,
model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo', // your preferred model
})
return result.choices[0]?.text
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error calling API:', error)
throw error
}
}
}
Or you could try with direct API request
ai: {
request: async (messages) => {
try {
const endpoint = process.env.API_ENDPOINT;
const deploymentId = process.env.DEPLOYMENT_ID;
const result = await makeApiRequest(endpoint, deploymentId, messages)
return result.choices[0]?.message.content
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error calling API:", error);
throw error;
}
}
}
...
async function getAccessToken() {
const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
const scope = "https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/.default";
try {
const accessToken = await credential.getToken(scope);
return `Bearer ${accessToken.token}`;
} catch (err) {
console.error("Failed to get access token:", err);
}
}
async function makeApiRequest(endpoint, deploymentId, messages) {
const token = await getAccessToken();
const url = `${endpoint}/openai/deployments/${deploymentId}/chat/completions?api-version=2024-06-01`;
const data = { messages };
try {
const response = await axios.post(url, data, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `${token}`
}
});
return response.data
} catch (err) {
console.error("API request failed:", err.response);
}
}
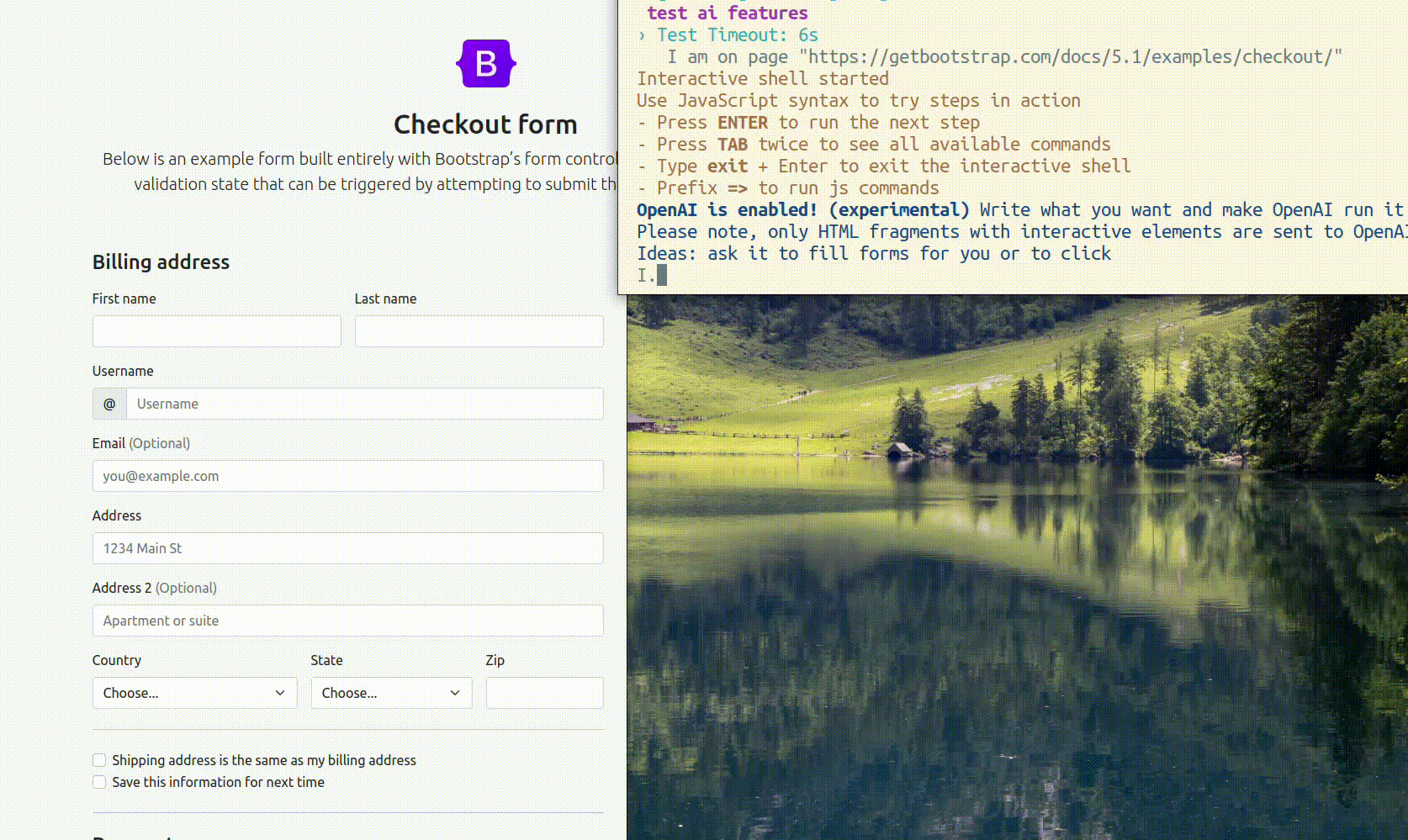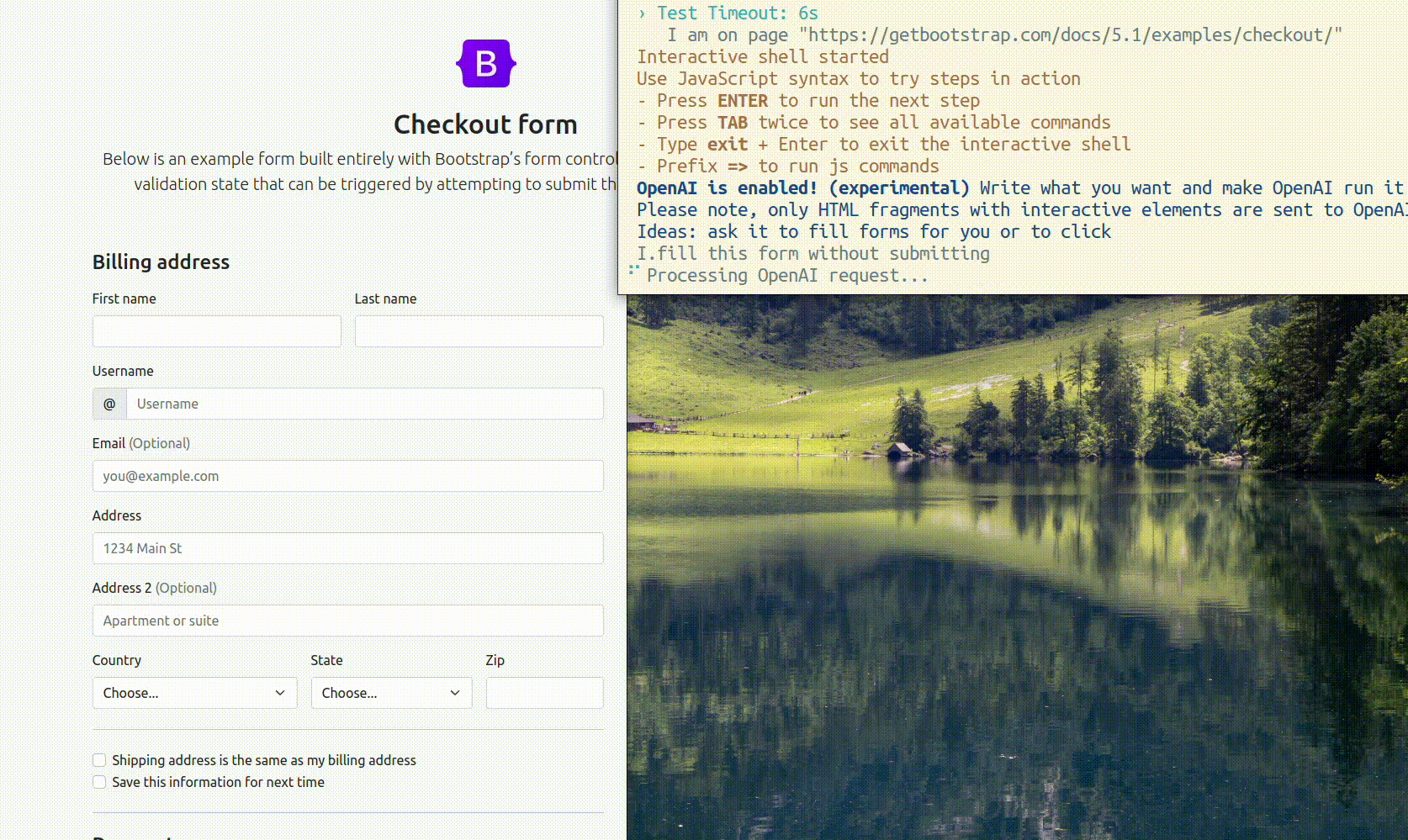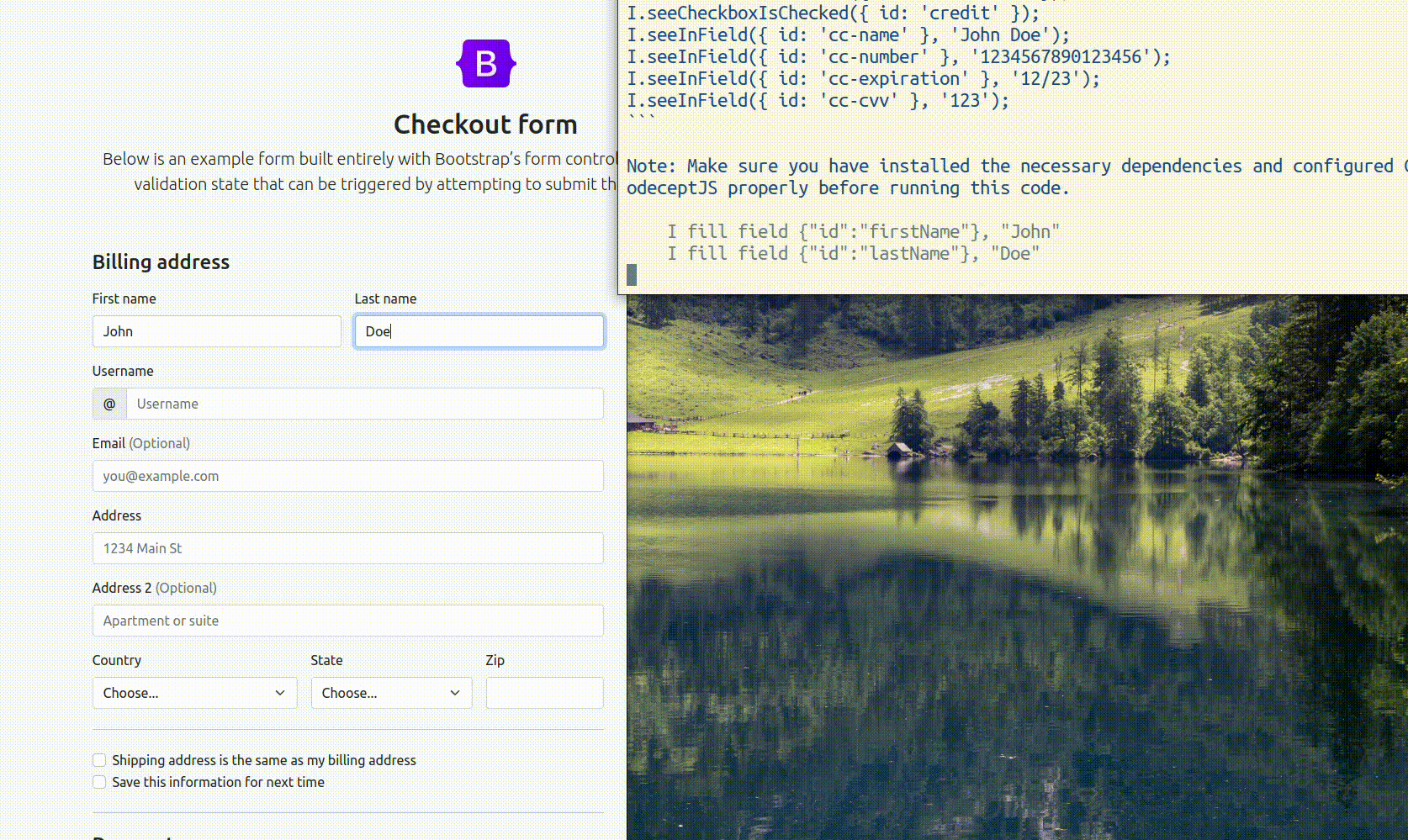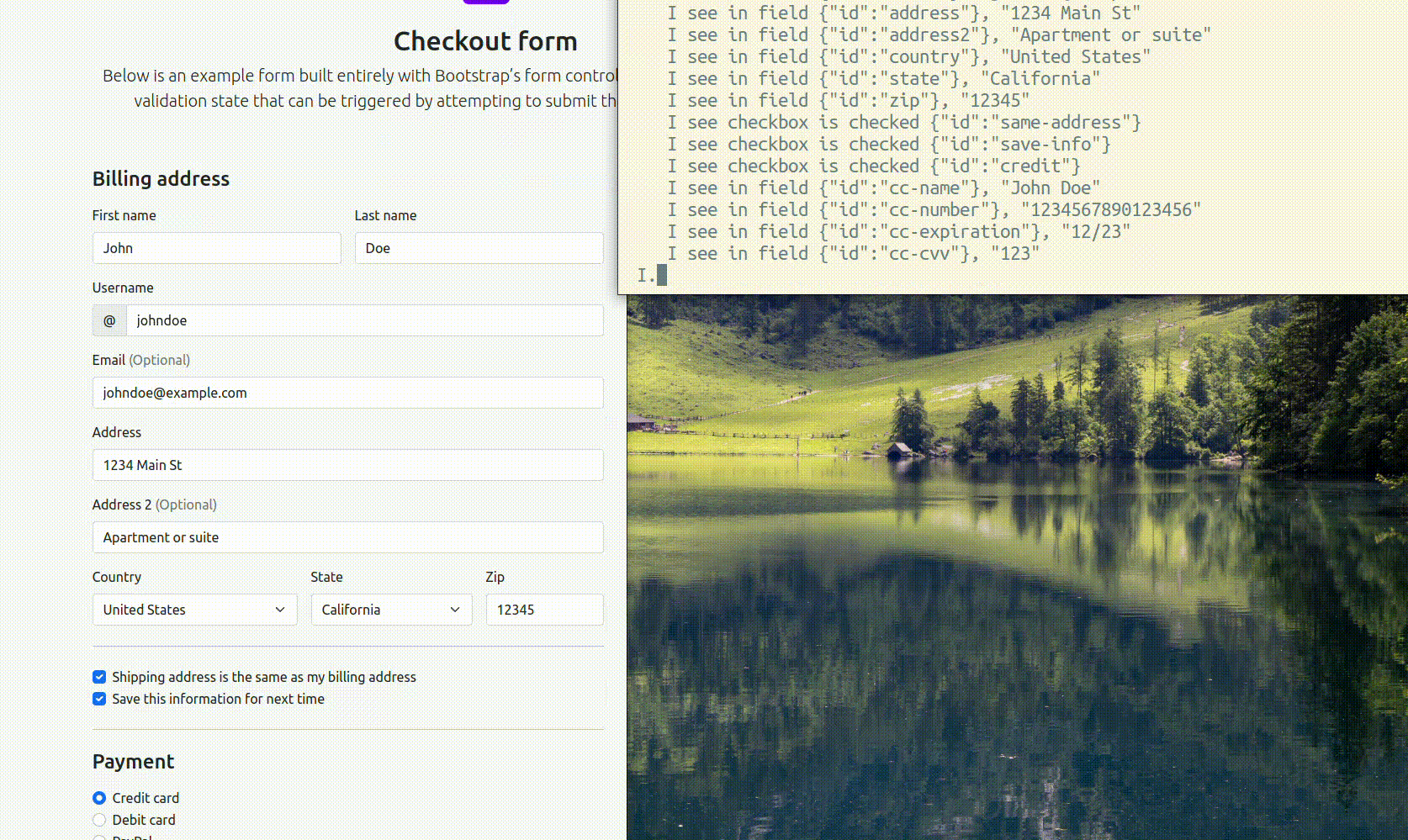
# Writing Tests with AI Copilot
If AI features are enabled when using interactive pause with pause() command inside tests:
For instance, let's create a test to try ai features via gt command:
npx codeceptjs gt
Name a test and write the code. We will use Scenario.only instead of Scenario to execute only this exact test.
Feature('ai')
Scenario.only('test ai features', ({ I }) => {
I.amOnPage('https://getbootstrap.com/docs/5.1/examples/checkout/')
pause()
})
Now run the test in debug mode with AI enabled:
npx codeceptjs run --debug --ai
When pause mode started you can ask GPT to fill in the fields on this page. Use natural language to describe your request, and provide enough details that AI could operate with it. It is important to include at least a space char in your input, otherwise, CodeceptJS will consider the input to be JavaScript code.
I.fill checkout form with valid values without submitting it
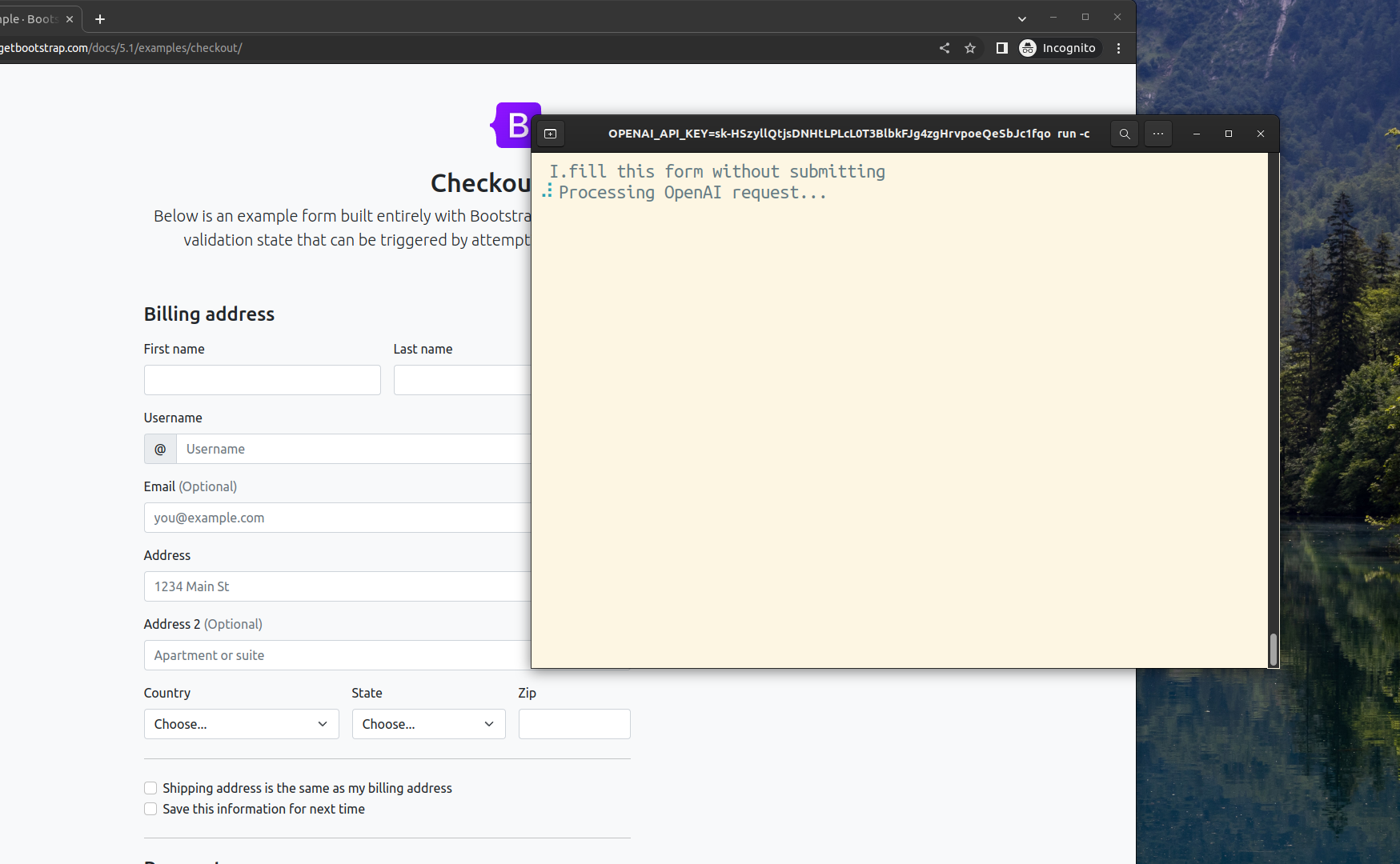
GPT will generate code and data and CodeceptJS will try to execute its code. If it succeeds, the code will be saved to history and you will be able to copy it to your test.
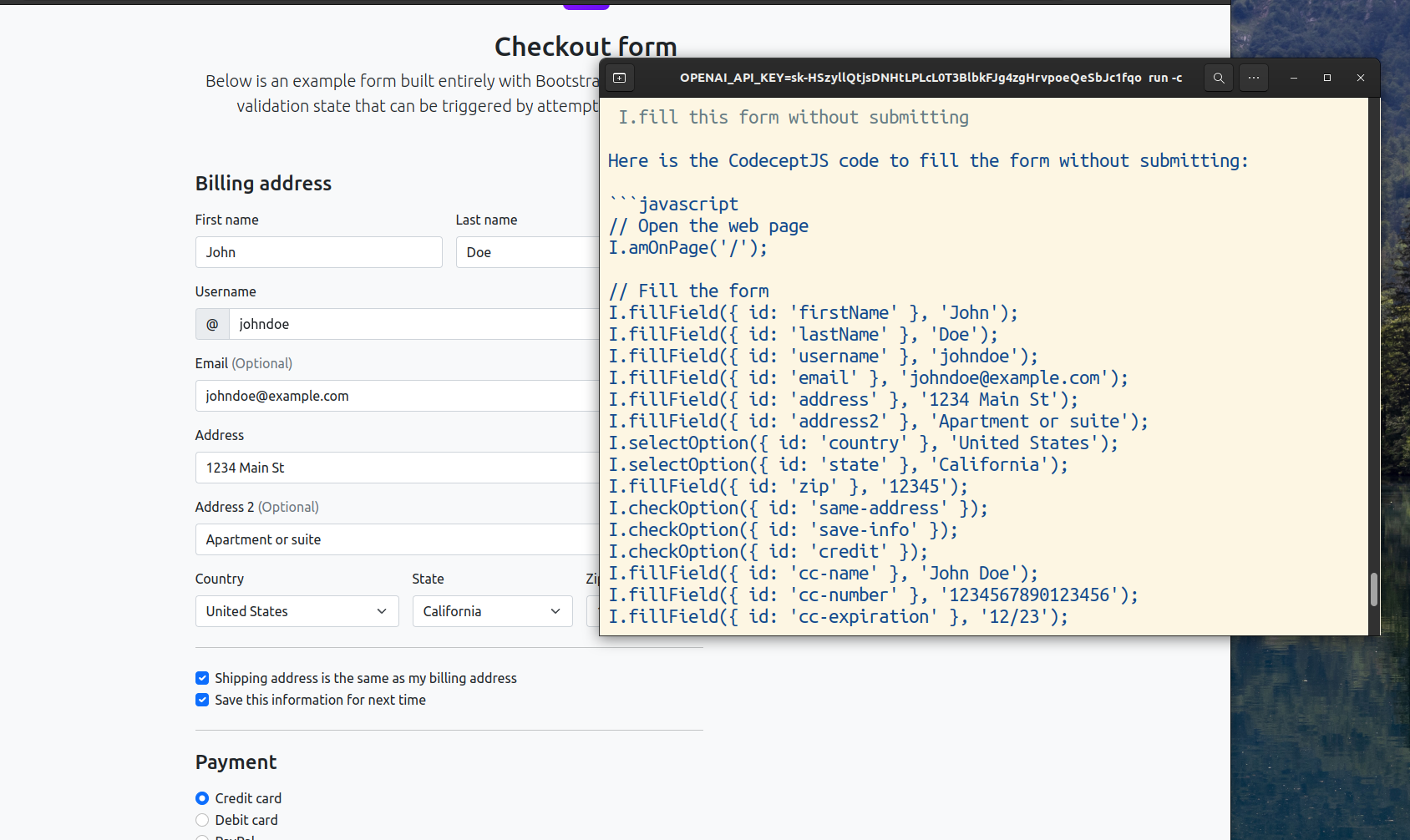
This AI copilot works best with long static forms. In the case of complex and dynamic single-page applications, it may not perform as well, as the form may not be present on HTML page yet. For instance, interacting with calendars or inputs with real-time validations (like credit cards) can not yet be performed by AI.
Please keep in mind that GPT can't react to page changes and operates with static text only. This is why it is not ready yet to write the test completely. However, if you are new to CodeceptJS and automated testing AI copilot may help you write tests more efficiently.
👶 Enable AI copilot for junior test automation engineers. It may help them to get started with CodeceptJS and to write good semantic locators.
# Self-Healing Tests
In large test suites, the cost of maintaining tests goes exponentially. That's why any effort that can improve the stability of tests pays itself. That's why CodeceptJS has concept of heal recipes, functions that can be executed on a test failure. Those functions can try to revive the test and continue execution. When combined with AI, heal recipe can ask AI provider how to fix the test. It will provide error message, step being executed and HTML context of a page. Based on this information AI can suggest the code to be executed to fix the failing test.
AI healing can solve exactly one problem: if a locator of an element has changed, and an action can't be performed, it matches a new locator, tries a command again, and continues executing a test. For instance, if the "Sign in" button was renamed to "Login" or changed its class, it will detect a new locator of the button and will retry execution.
You can define your own heal recipes that won't use AI to revive failing tests.
Heal actions **work only on actions like click, fillField, etc, and won't work on assertions, waiters, grabbers, etc. Assertions can't be guessed by AI, the same way as grabbers, as this may lead to unpredictable results.
If Heal plugin successfully fixes the step, it will print a suggested change at the end of execution. Take it as actionable advice and use it to update the codebase. Heal plugin is supposed to be used on CI, and works automatically without human assistance.
To start, make sure AI provider is connected, and heal recipes were created by running this command:
npx codeceptjs generate:heal
Heal recipes should be included into codecept.conf.js or codecept.conf.ts config file:
require('./heal')
exports.config = {
// ... your codeceptjs config
Then enable heal plugin:
plugins: {
heal: {
enabled: true
}
}
If you run tests in AI mode and a test fails, a request to AI provider will be sent
npx codeceptjs run --ai
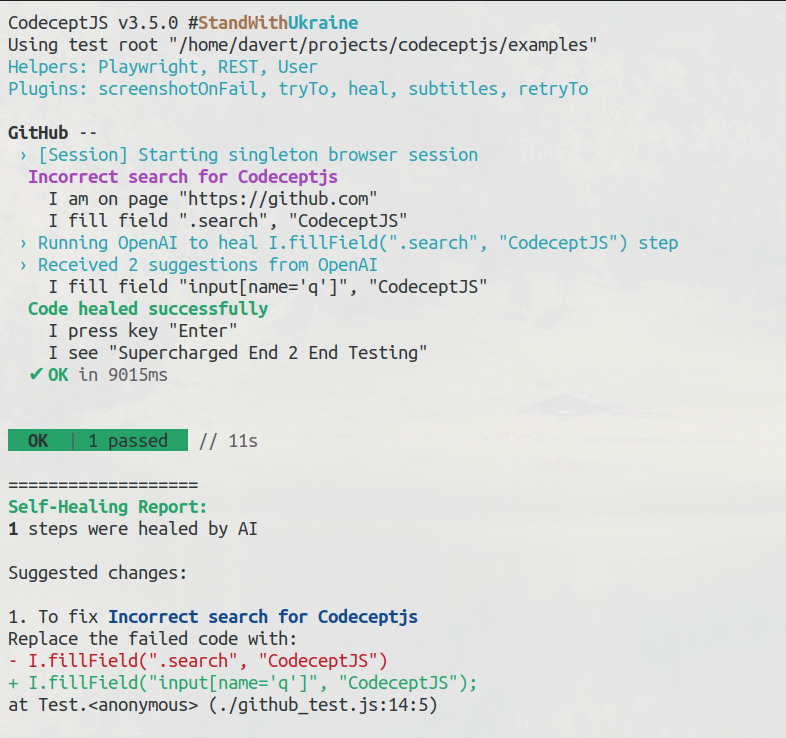
When execution finishes, you will receive information on token usage and code suggestions proposed by AI. By evaluating this information you will be able to check how effective AI can be for your case.
# Analyze Results
When running tests with AI enabled, CodeceptJS can automatically analyze test failures and provide insights. The analyze plugin helps identify patterns in test failures and provides detailed explanations of what went wrong.
Enable the analyze plugin in your config:
plugins: {
analyze: {
enabled: true,
// analyze up to 3 failures in detail
analyze: 3,
// group similar failures when 5 or more tests fail
clusterize: 5,
// enable screenshot analysis (requires modal that can analyze screenshots)
vision: false
}
}
When tests are executed with --ai flag, the analyze plugin will:
Analyze Individual Failures: For each failed test (up to the analyze limit), it will:
- Examine the error message and stack trace
- Review the test steps that led to the failure
- Provide a detailed explanation of what likely caused the failure
- Suggest possible fixes and improvements
Sample Analysis report:
When analyzing individual failures (less than clusterize threshold), the output looks like this:
🪄 AI REPORT:
--------------------------------
→ Cannot submit registration form with invalid email 👀
* SUMMARY: Form submission failed due to invalid email format, system correctly shows validation message
* ERROR: expected element ".success-message" to be visible, but it is not present in DOM
* CATEGORY: Data errors (password incorrect, no options in select, invalid format, etc)
* STEPS: I.fillField('#email', 'invalid-email'); I.click('Submit'); I.see('.success-message')
* URL: /register
The 👀 emoji indicates that screenshot analysis was performed (when
vision: true).
Cluster Similar Failures: When number of failures exceeds the clusterize threshold:
- Groups failures with similar error patterns
- Identifies common root causes
- Suggests fixes that could resolve multiple failures
- Helps prioritize which issues to tackle first
Categorize Failures: Automatically classifies failures into categories like:
- Browser/connection issues
- Network errors
- Element locator problems
- Navigation errors
- Code errors
- Data validation issues
- etc.
Clusterization output:
🪄 AI REPORT:
_______________________________
## Group 1 🔍
* SUMMARY: Element locator failures across login flow
* CATEGORY: HTML / page elements (not found, not visible, etc)
* ERROR: Element "#login-button" is not visible
* STEP: I.click('#login-button')
* SUITE: Authentication
* TAG: @login
* AFFECTED TESTS (4):
x Cannot login with valid credentials
x Should show error on invalid login
x Login button should be disabled when form empty
x Should redirect to dashboard after login
## Group 2 🌐
* SUMMARY: API timeout issues during user data fetch
* CATEGORY: Network errors (server error, timeout, etc)
* URL: /api/v1/users
* ERROR: Request failed with status code 504, Gateway Timeout
* SUITE: User Management
* AFFECTED TESTS (3):
x Should load user profile data
x Should display user settings
x Should fetch user notifications
## Group 3 ⚠️
* SUMMARY: Form validation errors on registration page
* CATEGORY: Data errors (password incorrect, no options in select, invalid format, etc)
* ERROR: Expected field "password" to have error "Must be at least 8 characters"
* STEP: I.see('Must be at least 8 characters', '.error-message')
* SUITE: User Registration
* TAG: @registration
* AFFECTED TESTS (2):
x Should validate password requirements
x Should show all validation errors on submit
If vision: true is enabled and your tests take screenshots on failure, the plugin will also analyze screenshots to provide additional visual context about the failure.
The analysis helps teams:
- Quickly understand the root cause of failures
- Identify patterns in failing tests
- Prioritize fixes based on impact
- Maintain more stable test suites
Run tests with both AI and analyze enabled:
npx codeceptjs run --ai
# Arbitrary Prompts
What if you want to take AI on the journey of test automation and ask it questions while browsing pages?
This is possible with the new AI helper. Enable it in your config file in helpers section:
// inside codecept.conf
helpers: {
// Playwright, Puppeteer, or WebDrver helper should be enabled too
Playwright: {
},
AI: {}
}
AI helper will be automatically attached to Playwright, WebDriver, or another web helper you use. It includes the following methods:
askGptOnPage- sends GPT prompt attaching the HTML of the page. Large pages will be split into chunks, according tochunkSizeconfig. You will receive responses for all chunks.askGptOnPageFragment- sends GPT prompt attaching the HTML of the specific element. This method is recommended overaskGptOnPageas you can reduce the amount of data to be processed.askGptGeneralPrompt- sends GPT prompt without HTML.askForPageObject- creates PageObject for you, explained in next section.
askGpt methods won't remove non-interactive elements, so it is recommended to manually control the size of the sent HTML.
Here are some good use cases for this helper:
- get page summaries
- inside pause mode navigate through your application and ask to document pages
- etc...
// use it inside test or inside interactive pause
// pretend you are technical writer asking for documentation
const pageDoc = await I.askGptOnPageFragment('Act as technical writer, describe what is this page for', '#container')
As of now, those use cases do not apply to test automation but maybe you can apply them to your testing setup.
# Generate PageObjects
Last but not the least. AI helper can be used to quickly prototype PageObjects on pages browsed within interactive session.
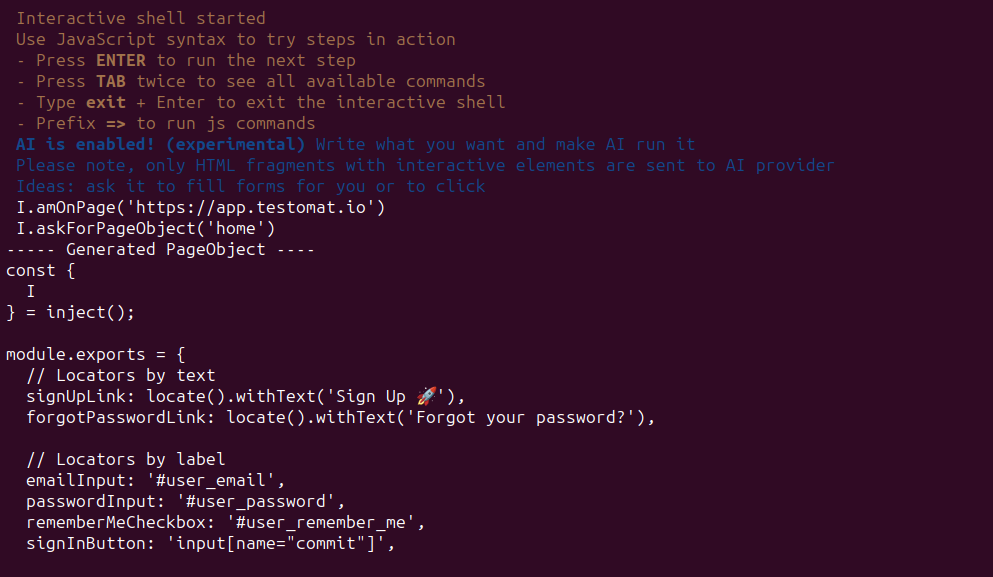
Enable AI helper as explained in previous section and launch shell:
npx codeceptjs shell --ai
Also this is availble from pause() if AI helper is enabled,
Ensure that browser is started in window mode, then browse the web pages on your site.
On a page you want to create PageObject execute askForPageObject() command. The only required parameter is the name of a page:
I.askForPageObject('login')
This command sends request to AI provider should create valid CodeceptJS PageObject. Run it few times or switch AI provider if response is not satisfactory to you.
You can change the style of PageObject and locator preferences by adjusting prompt in a config file
When completed successfully, page object is saved to output directory and loaded into the shell as page variable so locators and methods can be checked on the fly.
If page object has signInButton locator you can quickly check it by typing:
I.click(page.signInButton)
If page object has clickForgotPassword method you can execute it as:
=> page.clickForgotPassword()
Here is an example of a session:
Page object for login is saved to .../output/loginPage-1718579784751.js
Page object registered for this session as `page` variable
Use `=>page.methodName()` in shell to run methods of page object
Use `click(page.locatorName)` to check locators of page object
I.=>page.clickSignUp()
I.click(page.signUpLink)
I.=> page.enterPassword('asdasd')
I.=> page.clickSignIn()
You can improve prompt by passing custom request as a second parameter:
I.askForPageObject('login', 'implement signIn(username, password) method')
To generate page object for the part of a page, pass in root locator as third parameter.
I.askForPageObject('login', '', '#auth')
In this case, all generated locators, will use #auth as their root element.
Don't aim for perfect PageObjects but find a good enough one, which you can use for writing your tests.
All created page objects are considered temporary, that's why saved to output directory.
Rename created PageObject to remove timestamp and move it from output to pages folder and include it into codecept.conf file:
include: {
loginPage: "./pages/loginPage.js",
// ...
# Advanced Configuration
GPT prompts and HTML compression can also be configured inside ai section of codecept.conf file:
ai: {
// define how requests to AI are sent
request: (messages) => {
// ...
}
// redefine prompts
prompts: {
// {}
},
// how to process HTML content
html: {
// {}
}
// limit the number of tokens to be
// used during one session
maxTokens: 100000
}
Default prompts for healing steps or writing steps can be re-declared. Use function that accepts HTML as the first parameter and additional information as second and create a prompt from that information. Prompt should be an array of messages with role and content data set.
ai: {
prompts: {
writeStep: (html, input) => [{ role: 'user', content: 'As a test engineer...' }]
healStep: (html, { step, error, prevSteps }) => [{ role: 'user', content: 'As a test engineer...' }]
generatePageObject: (html, extraPrompt = '', rootLocator = null) => [{ role: 'user', content: 'As a test engineer...' }]
}
}
HTML is processed before sending it to GPT to reduce the number of tokens used. You may need to adjust default settings to work with your application. For instance, the default strategy may remove some important elements, or contrary keep HTML elements that have no use for test automation.
Here is the default config:
ai: {
html: {
maxLength: 50000,
simplify: true,
minify: true,
interactiveElements: ['a', 'input', 'button', 'select', 'textarea', 'option'],
textElements: ['label', 'h1', 'h2'],
allowedAttrs: ['id', 'for', 'class', 'name', 'type', 'value', 'tabindex', 'aria-labelledby', 'aria-label', 'label', 'placeholder', 'title', 'alt', 'src', 'role'],
allowedRoles: ['button', 'checkbox', 'search', 'textbox', 'tab'],
}
}
maxLength: the size of HTML to cut to not reach the token limit. 50K is the current default but you may try to increase it or even set it to null.simplify: should we process HTML before sending to GPT. This will remove all non-interactive elements from HTML.minify: should HTML be additionally minified. This removed empty attributes, shortens notations, etc.interactiveElements: explicit list of all elements that are considered interactive.textElements: elements that contain text which can be used for test automation.allowedAttrs: explicit list of attributes that may be used to construct locators. If you use specialdata-attributes to enable locators, add them to the list.allowedRoles: list of roles that make standard elements interactive.
It is recommended to try HTML processing on one of your web pages before launching AI features of CodeceptJS.
To do that open the common page of your application and using DevTools copy the outerHTML of <html> element. Don't use Page Source for that, as it may not include dynamically added HTML elements. Save this HTML into a file and create a NodeJS script:
const { removeNonInteractiveElements } = require('codeceptjs/lib/html')
const fs = require('fs')
const htmlOpts = {
interactiveElements: ['a', 'input', 'button', 'select', 'textarea', 'label', 'option'],
allowedAttrs: ['id', 'for', 'class', 'name', 'type', 'value', 'aria-labelledby', 'aria-label', 'label', 'placeholder', 'title', 'alt', 'src', 'role'],
textElements: ['label', 'h1', 'h2'],
allowedRoles: ['button', 'checkbox', 'search', 'textbox', 'tab'],
}
html = fs.readFileSync('saved.html', 'utf8')
const result = removeNonInteractiveElements(html, htmlOpts)
console.log(result)
Tune the options until you are satisfied with the results and use this as html config for ai section inside codecept.conf file.
It is also recommended to check the source of removeNonInteractiveElements (opens new window) and if needed propose improvements to it.
For instance, if you use data-qa attributes to specify locators and you want to include them in HTML, use the following config:
{
// inside codecept.conf.js
ai: {
html: {
allowedAttrs: ['data-qa', 'id', 'for', 'class', 'name', 'type', 'value', 'aria-labelledby', 'aria-label', 'label', 'placeholder', 'title', 'alt', 'src', 'role']
}
}
}
# Debugging
To debug AI features run tests with DEBUG="codeceptjs:ai" flag. This will print all prompts and responses from AI provider
DEBUG="codeceptjs:ai" npx codeceptjs run --ai
or if you run it in shell mode:
DEBUG="codeceptjs:ai" npx codeceptjs shell --ai